METAAL
- 21 februari 2013
- Reacties uitgeschakeld voor METAAL
- in METAAL
Objective
The objective of this work package is to further develop knowledge of 3D metal printing and to realize applications. Known techniques for 3D metal printing can be broadly divided into three types:
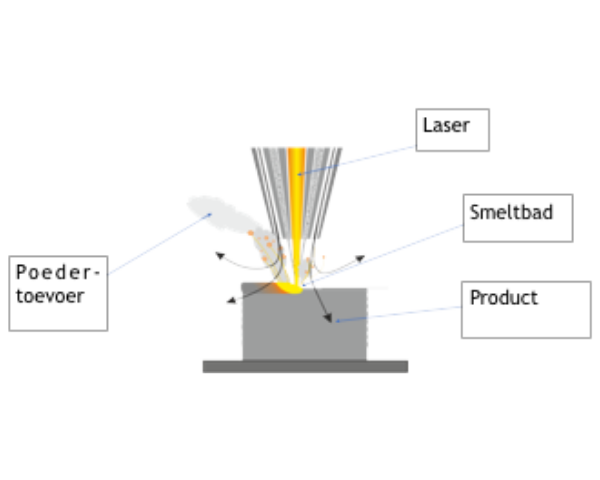
- Direct energy deposition (DED), in which parts are built up by spraying molten metal onto a surface with a welding head. This can be done with different energy sources, such as a laser, an electron beam, or an electric arc, as shown in the figure below.
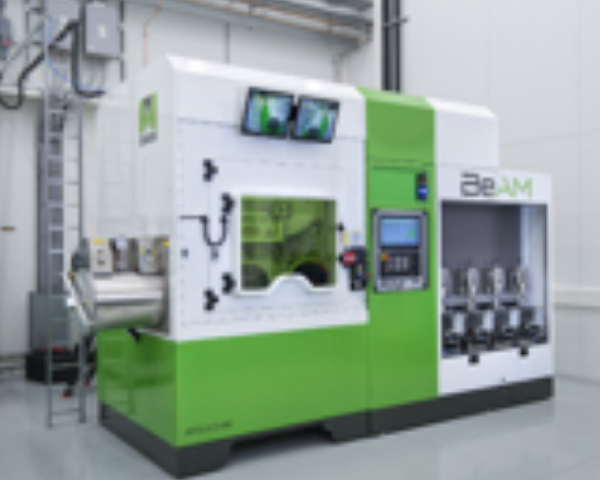
- DED facilities are often suitable for the manufacture of larger parts and the finished material is of high quality metallurgical. This technique also allows printing on existing shapes and repairs can be carried out. NLR has a DED system.
- Powder bed fusion (PBF), in which parts are manufactured by fusing local material in a bed of metal powder using a laser or electron beam. PBF techniques are relatively accurate and the end material is of high metallurgical quality. Systems that use this technique are available at, among others, the Innovation Cluster Drachten and the University of Groningen.
- Bindmiddel-gebaseerde printtechnieken, waarbij een geprint onderdeel bestaat uit metaalpoeder dat m.b.v. een kunststof bindmiddel bij elkaar wordt gehouden. D.m.v. sinteren wordt het bindmiddel vervolgens uitgebrand en het onderdeel verdicht zodat een zuiver metalen onderdeel wordt verkregen. Technieken van dit soort vormen geen categorie op zich, maar vallen onder verschillende categorieën. Ze onderscheiden zich door de relatief lage kostprijs van vervaardigde onderdelen en specifieke mogelijk- en onmogelijkheden m.b.t. ontwerpvrijheid. Binder3D en het NLR beschikken over een bindmiddel-gebaseerd systeem (dat gebruik maakt metaalpoeder-gevuld filament).
Bovengenoemde categorieën technieken hebben elk hun sterke punten en zwakke punten en worden zodoende beschouwd als zijnde complementair aan elkaar. Strategisch gezien is het versterken van kennis van alle drie deze categorieën hiermee het meest waardevol.
Projectactiviteiten
Activiteiten m.b.t. 3D-metaalprinttechnieken zijn als volgt:
- DED-techniek: kennis ontwikkelen van verschillende varianten van de DED-techniek met het doel om te onderzoeken hoe deze van meerwaarde zijn binnen de aan het project deelnemende bedrijven. Voor het bij het NLR beschikbare DED-systeem (zie onderstaande afbeelding) zal de focus liggen op procesonderzoek en het realiseren van toepassingen.
- PBF technique: developing knowledge of process quality and stability with the aim of developing a high-quality, certified printing process. In addition, realizing applications of this printing technique. Use will be made of the PBF facilities available at the participants.
- Binder-based printing techniques: developing state-of-the-art knowledge of this category of printing techniques with the aim of making it possible to manufacture metal parts cost-efficiently. For systems using filaments, the focus will be on realizing applications, while for systems using material powders, the focus will initially be on acquiring knowledge about the possibilities of commercially available systems and services.
- Because 3D printing offers added value in particular in cases where complex shapes or functionalities are desired, there will be interaction with the Design Methods work package.
business case
Collaboration in the field of 3D metal printing helps the manufacturing industry in the Northern Netherlands in various ways:
- Companies whose core activity is the manufacture of metal parts can use 3D metal printing as a production technique. Because 3D metal printing is opposed to machining techniques (such as milling and turning) in both technique and possibilities, such companies now have access to a production technique with completely new possibilities. They can use these to manufacture new types of parts, e.g. parts with a very high degree of complexity.
- For companies that manufacture parts or products in large series (in metal or plastic), 3D printing can be used to improve their manufacturing processes, for example by producing highly complex moulds, lightweight robotic hands, or other tools. In addition, with binder-based printing techniques it is possible to make metal parts in small series at a cost that is lower than when using casting or powder injection molding. Serial production of personalized products is also an option.
- Companies that design their own products but do not manufacture parts themselves can use 3D metal printing to create functional prototypes and thus speed up their product development process. In addition, knowledge of 3D metal printing is important for them to manufacture parts that a specialized supplier for 3D printed parts could manufacture for them.
Involved in this work package are NLR, Stork, NTS-Norma, Philips, Landes, University of Groningen, Binder3D, and ASTRON.